Assessment Process
Assessment Process
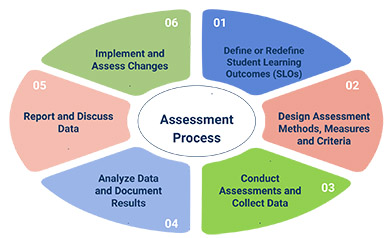
In order to continuously improve student learning and academic programs, Alfaisal University faculty engage in a rigorous assessment process and use the results to make informed decisions about future teaching and learning. The graphic below outlines in detail the steps needed to conduct effective program/course assessments. Please note that all assessments cycles are conducted using this basic process, with some variations based on the program/department type. Further details of each step are provided in the subsequent sections below.
In this step, faculty members clarify the intended student learning objectives (SLOs) and map them to the program and course outcomes. The faculty defines the knowledge, skills, and competencies that students should acquire as a result of their educational experience, ensuring that they are specific, measurable, achievable, and appropriate for the students' level. To define learning outcomes, instructors must consider the goals of the educational program, the standards and expectations of the field, and the needs and abilities of the students. This step also involves aligning the learning outcomes with the program outcomes, instructional materials, and assessments used to evaluate student progress, creating a cohesive and coherent educational experience for the students
During the second step of the assessment cycle, the faculty determines the most appropriate methods for evaluating student performance and establishes clear standards for success by determining the criteria. Both direct and indirect assessment methods are considered, with the goal of accurately evaluating all aspects of student learning.
- Direct assessment methods, such as written exams, presentations, projects, portfolios, or performance tasks, are selected because they align with the learning outcomes being assessed and reflect the level of student understanding and development. These assessments provide a clear and direct representation of student knowledge and skills and are an important tool for evaluating the effectiveness of the instructional program.
- Indirect assessment methods, such as surveys, questionnaires, and interviews, are used to measure the conditions that support student learning, such as student engagement and satisfaction. This type of assessment provides a deeper understanding of student experiences and can be used to identify areas for improvement in the instructional program.
In addition to selecting the assessment methods, the faculty also establishes the criteria for determining successful learning. This includes identifying the required knowledge, skills, and competencies, as well as the evaluation standards. These criteria can be clearly communicated to students through the use of rubrics, which provide a detailed breakdown of the expectations for student performance.
During the third step of the assessment cycle, faculty members administer assessments to collect data. This step involves giving written exams, evaluating student presentations, grading projects, or using any other appropriate assessment method. It is important for faculty members to ensure that the assessments are administered fairly and consistently, and that all students have a clear understanding of the expectations and criteria for evaluation. Additionally, instructors must make sure that the assessments are accessible to all students, regardless of their learning styles or disabilities. This helps to ensure that the data collected is accurate and representative of student learning and performance.
This step involves carefully examining the collected data to identify patterns and make inferences about the individual's abilities and characteristics. As faculty analyze and interpret the data, it is important to consider the following:
- What key or unique patterns did you find in the data? These patterns can provide important insights into the individual's strengths, weaknesses, and overall abilities.
- What do these patterns reveal about the students or student learning? The patterns you identify can shed light on the individual's performance, abilities, and learning style, and can provide valuable information for making informed decisions about their future.
- What interpretations and recommendations can be derived from the results? By interpreting the data and making connections between the patterns you have identified and the individual's abilities, you can make informed recommendations about their next steps and support their growth and development.
- Are the interpretations and recommendations evident from the data? It is important to ensure that any interpretations and recommendations you make are based on the data and are not influenced by personal biases or preconceptions. This can be achieved by conducting a thorough and objective analysis of the data and carefully considering all of the patterns and relationships that you have identified.
During this step, the faculty member turns the data collected during the assessment process into actionable information by analyzing the results, and presenting them to relevant stakeholders, including faculty, administrators, and sometimes students. This can be done through various means, such as presentations, reports, or meetings. The purpose of this stage is to provide a clear picture of the effectiveness of the programs or courses, including their strengths and weaknesses. This allows stakeholders to understand what is working well and what needs improvement. In some cases, the results may highlight the need for changes in the curriculum, teaching methods, course materials, or physical learning environment. It is important that the results are communicated in a transparent and accessible manner to all stakeholders to promote buy-in and ensure everyone is aware of the findings and changes that need to be made. This also allows for open and honest discussions about the results and any concerns or questions that may arise.
At this stage, the faculty member and the institution take the findings from the assessment process and put them into action by implementing changes to their programs and courses. The changes made in this stage are designed to address the strengths and weaknesses identified in previous stages of the cycle, and to align with the goals and expectations set in the first stage of defining or redefining student learning outcomes. For example, if the results of the assessment process reveal a struggle with a particular aspect of a program or course, the institution may revise the curriculum, teaching methods, course materials, or physical learning environment to better support student learning.
Additionally, this stage is an opportunity for the institution to continuously improve their programs and courses. By regularly assessing the effectiveness of their programs and courses and making changes based on the results, the institution can ensure that they are meeting their learning outcomes and providing students with the best possible educational experience. In conclusion, the implementation and assessment of changes stage is a critical part of the academic assessment cycle and closely tied to the first stage of defining or redefining student learning outcomes. This stage allows the institution to close the loop on the process and continuously improve their programs and courses to better support student learning and success.